This equilibrium practice problem set includes questions on writing the equilibrium constant of given chemical reactions, determining the value of the equilibrium constant based on the concentrations and partial pressures of gases, deriving a new expression for an equilibrium constant from separate reactions, converting between Kc and Kp, calculating the quotient and determining the course of the reaction, calculations of concentrations based on the quotient and equilibrium constant, as well as working on equilibrium reactions based on the Le Châtelier’s principle.
The links to the corresponding articles are provided herein:
Write the equilibrium expression (K) for each of the following reactions.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
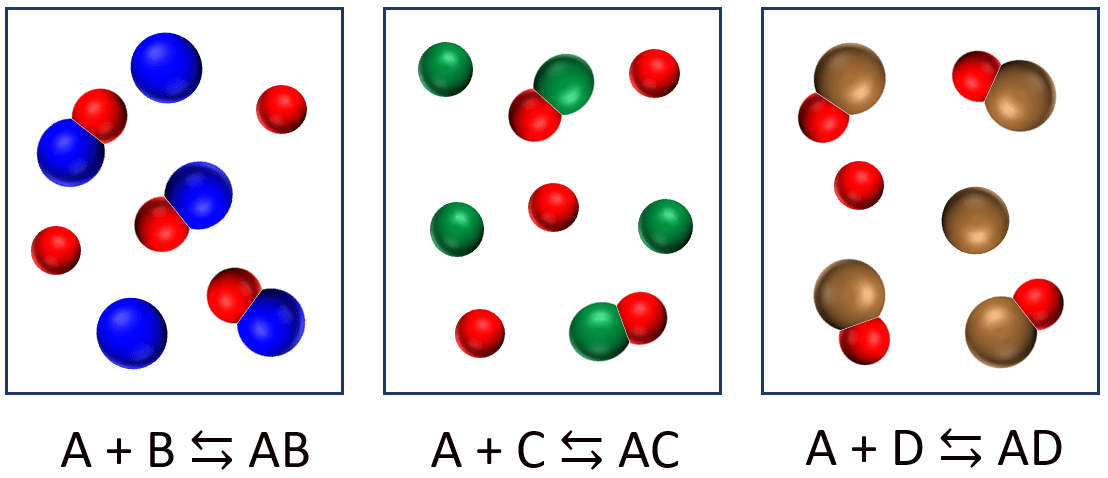
Tree different reactions are represented in the diagram below. The reaction equations can be written as A + X ⇆ AX (X = B, C, or D).

(a) Which reaction has the largest equilibrium constant? (b) Which reaction has the smallest equilibrium constant?
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
The following graph represents an initial mixture of N2 and H2 at high temperature and pressure:
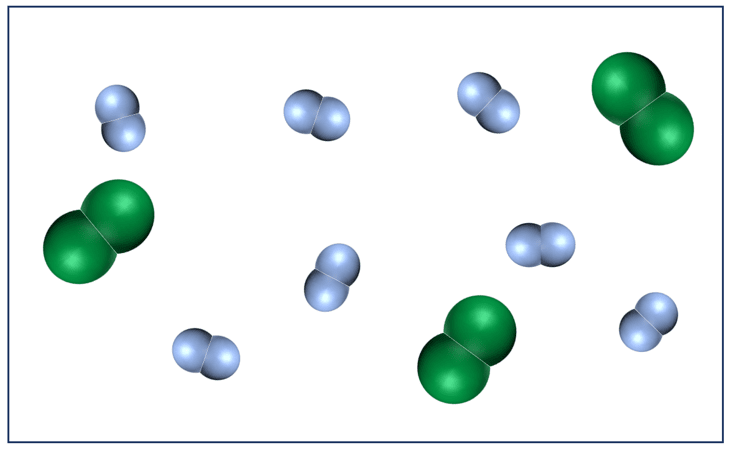
The gases react to form ammonia gas (NH3) as represented by the following concentration profile:
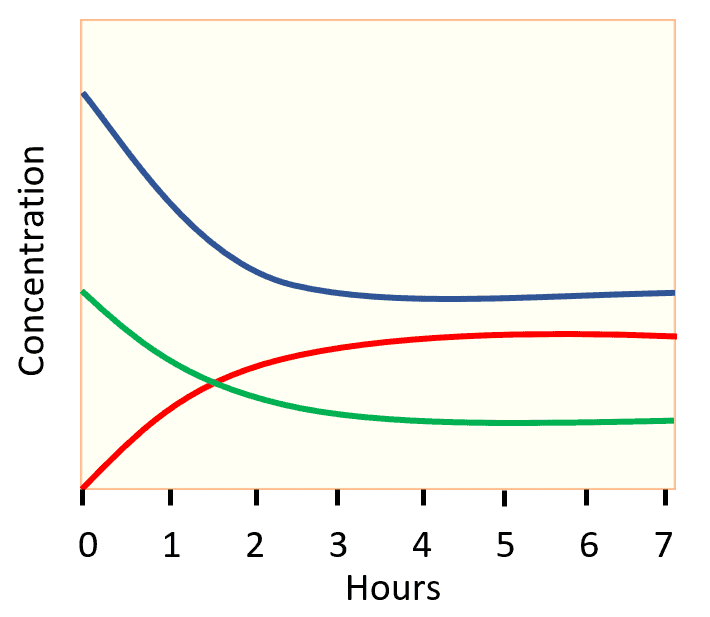
a) Label each plot on the graph as H2, N2, or NH3, and explain your answers.
b) What information do the relative shapes of the plots tell us?
c) At what time is equilibrium reached?
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
At a particular temperature, it is determined for the reaction
that at equilibrium, the concentrations are as follows: [NO(g)] = 3.2 x 10 -3 M, [H2(g)] = 6.7 x 10 -6 M, [N2(g)] = 4.8 x 10 -2 M, and [H2O(g)] = 2.4 x 10 -2 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant K for the reaction at this temperature?
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Given the equilibrium concentrations, calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for the reaction between CO2 and H2 that produces methanol and water at high temperature.
[CO2] = 0.061 M, [H2] = 0.079 M, [CH3OH] = 4.7 x 10 2 M, and [H2O] = 5.7 x 10 4 M Calculate the value of K for the reaction.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
The reaction for converting methane to acetylene has an equilibrium constant of K = 0.154 at 2000 K.
Calculate the equilibrium constant for this process if the reaction is represented as follows:
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
The following reaction has an equilibrium constant of Kp = 4.42 x 10 -5 at 298 K:
Calculate the equilibrium constant for this process if the reaction is represented as follows:
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
The equilibrium constant values for the reactions below were determined at a certain temperature:
Using these data, determine the equilibrium constant Kc for the following reaction:
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
The equilibrium constant values for the reactions below were determined at a certain temperature:
Using these data, determine the equilibrium constant Kc for the following reaction:
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
The following equilibrium pressures were observed at a certain temperature for the Haber process
Calculate the value for the equilibrium constant Kp at this temperature.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Consider the following reactions:
In which reaction are the K and Kp equal?
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
At 300 K, the equilibrium concentrations for the following reaction are [CH3OH] = 0.240 M, [CO] = 0.350 M, and [H2] = 1.65 M for the reaction
Calculate Kp at this temperature.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Given the equilibrium constant, calculate Kp for each of the following reactions at 298 K.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Calculate the Kc for each reaction at 298 K.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
This content is available to registered users only. Click here to Register! By joining Chemistry Steps, you will gain instant access to the Answers and Solutions for all the Practice Problems, Quizzes, and the powerful set of General Chemistry 1 and 2 Summary Study Guides.
Consider the reaction between nitrogen and hydrogen gases:
Using the data given in the table, complete the missing numbers assuming that all concentrations are measured at equilibrium.
 Preparing for orgo organic chemistry after General Chemistry" width="914" height="645" />
Preparing for orgo organic chemistry after General Chemistry" width="914" height="645" />
Chemistry Steps LLC
General Chemistry Articles, Study Guides, and Practice Problems.
5900 Balcones Drive, Austin, TX 78731
info@chemistrysteps.com