
Project Quality Management is the 5th knowledge area within the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK). It contains the knowledge and processes required to ensure the highest quality products and deliverables are produced by the project. Although the highest quality should always be a goal, the highest grade is not necessarily so.
For example, a particular child’s toy might be high grade (many features, etc.), but if the parts break easily the quality could be unacceptable.

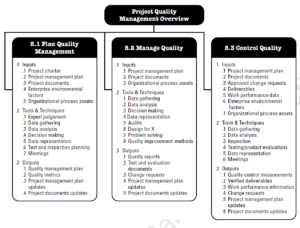
There are three processes within this knowledge area:
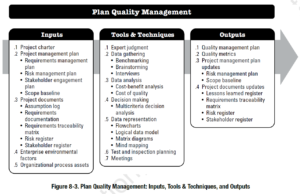
This process involves the determination of the quality standards that govern the project deliverables and/or product and how the project will achieve compliance to those standards. Many projects have standards that are given to them directly, such as design standards for buildings. However, many other standards often exist which are not explicitly stated but expected to be complied with. The project manager could purchase the applicable standards from organizations such as ASTM, IEEE, or ANSI to ensure a complete set.
The main output of this process is a quality management plan which dictates the quality standards and outlines how those standards will be met as well as the quality assurance and quality control activities.
PMBOK, 6th Edition, Section 8.1.3.1, “Quality Management Plan”
The quality management plan is a component of the project management plan that describes how the applicable policies, procedures, and guidelines will be implemented to achieve the quality objectives. It describes the activities and resources necessary for the project management team to achieve the quality objectives set for the project.
The quality management plan may be formal or informal, detailed, or broadly framed. The style and detail of the quality management plan are determined by the requirements of the project.
 Inputs
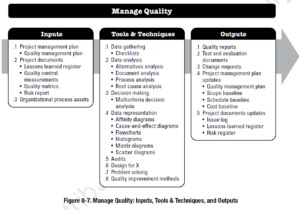
InputsManage Quality is the process of auditing the quality requirements and the results from quality control measurements to ensure that appropriate quality standards and operational definitions are used. The quality audits test and/or confirm that the system is functioning correctly. Quality assurance should always be based on a foundation of continuous improvement.
 Inputs
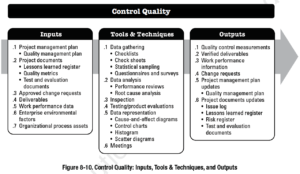
InputsQuality Control is the process of monitoring and recording results of executing the quality activities to assess performance and recommend necessary changes. In short, it is the measurement of defects.
 Inputs
Inputs